Article page Header
20.03.2023 | Laerdal Medical
Laerdal Invest owns, develops and manages the local production and office sites in Norway through Tanke Svilandsgate 30-36 AS and Vestre Svanholmen 3 AS.
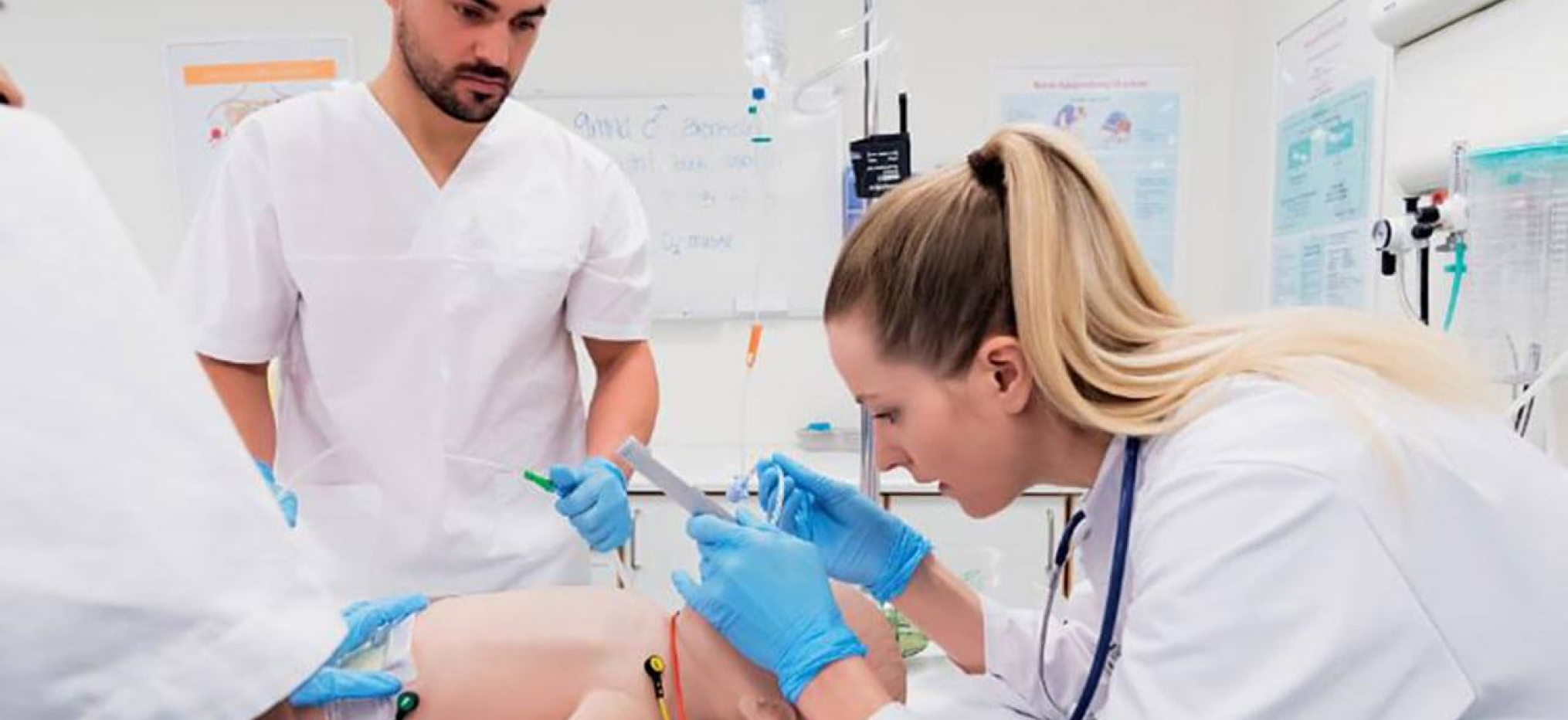
Sudden cardiac arrest in the community is still a major cause of death despite significant advances in prevention and therapy over the last 60 years. The visual metaphor for treatment of such cardiac arrests has evolved through advances in medical and educational science into what is called the Chain of Survival. Each circle represents one step in the chain from the bystander’s recognition of the emergency; calling for help and being coached by the dispatcher in applying CPR; high performance CPR and early defibrillation by first responders or Emergency Medical Technicians; further therapy and stabilisation by paramedics; and finally hospital care.
The Global Potential
Although the emphasis until the last decade was on HICs, cardiac arrest is not only a problem in such societies. In fact, 86% of all global cardiac arrests are estimated to occur in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) where survival rates are lowest and the opportunity for impact is greatest. Numerous studies show that survival in HICs averages about 50 per million population with the highest performing centres exceeding 100 per million population. The survival data for LMICs is poor but the current average survival rate is believed to be well under 5 per million population. The table shows the potential for lives to be saved if everyone approached the performance of the best: a total of more than 600,000 extra lives per annum.
The Global Potential
- Harnessing the power of cost-effective information and communication technologies to enhance health education, people-centred health services and health information systems;
- Scaling up transformative, high-quality education and lifelong learning so that all health workers have skills that match the health needs of populations and can work to their full potential
- Harnessing the power of cost-effective information and communication technologies to enhance health education, people-centred health services and health information systems;
- Scaling up transformative, high-quality education and lifelong learning so that all health workers have skills that match the health needs of populations and can work to their full potential
- Harnessing the power of cost-effective information and communication technologies to enhance health education, people-centred health services and health information systems;
- Scaling up transformative, high-quality education and lifelong learning so that all health workers have skills that match the health needs of populations and can work to their full potential
The Global Potential
- Harnessing the power of cost-effective information and communication technologies to enhance health education, people-centred health services and health information systems.
- Scaling up transformative, high-quality education and lifelong learning so that all health workers have skills that match the health needs of populations and can work to their full potential